📘CCNA 200-301 v1.1, CompTIA Network+ (N10-009)
1.1.a Routers
🔹 What is a Router?
A router is a device that connects different networks together.
- It looks at the destination IP address inside a packet.
- It decides where to send the packet next.
- Without a router, devices in different networks (or subnets) cannot communicate.
🔹 What Does a Router Do?
- Connect networks
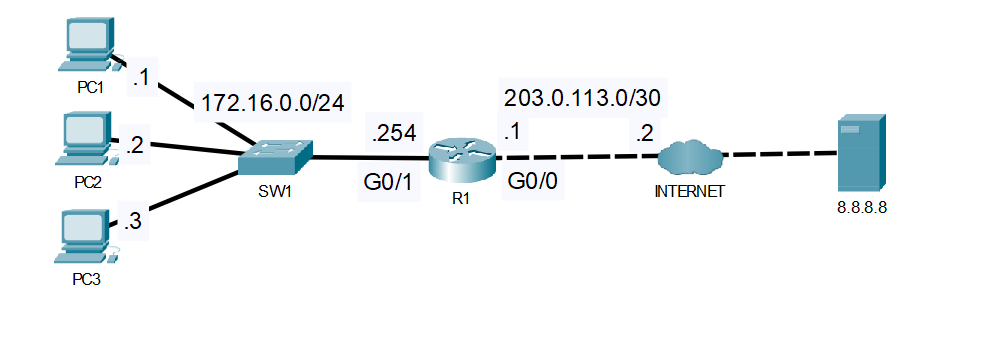
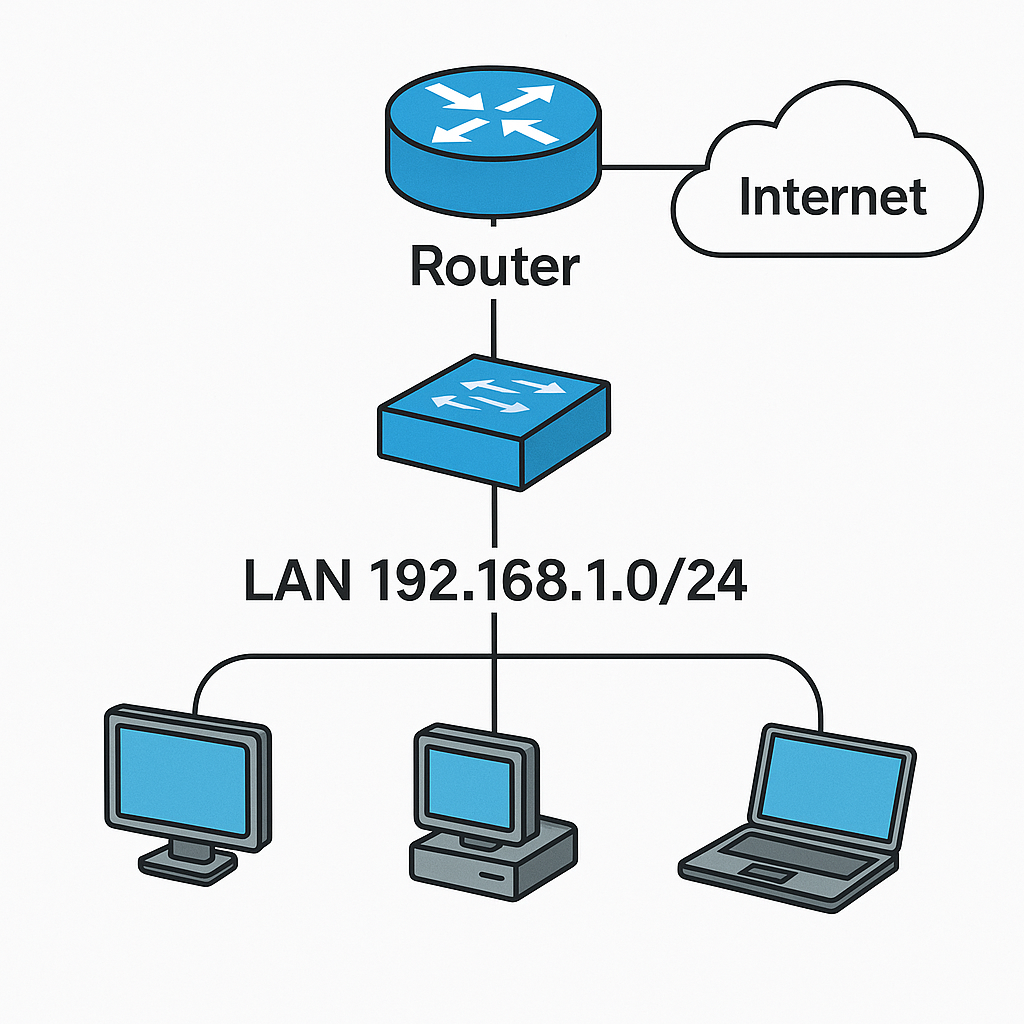
- Example: Connects your school network (LAN) to the internet (WAN).
- Example: Connects Building A network (192.168.1.0/24) to Building B network (192.168.2.0/24).
- Path selection
- The router checks its routing table.
- If there are many possible paths, it chooses the best one.
- This can be done with static routes (manually added) or dynamic routing protocols (OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, BGP).
- Inter-VLAN routing
- If you create VLANs in a switch, a router (or Layer 3 switch) is needed to let devices in different VLANs talk to each other.
- Security and filtering
- Routers can use ACLs (Access Control Lists) to allow or block traffic.
- This is often the first line of defense before traffic enters your network.
- NAT (Network Address Translation)
- Routers can hide private IP addresses behind one public IP.
- This is how home and school networks access the internet.
🔹 Router vs Switch
Yes ✅.
| Feature | Router | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Works at | Layer 3 (Network) | Layer 2 (Data Link) |
| Uses | IP addresses | MAC addresses |
| Purpose | Connects different networks | Connects devices in the same network |
| Example | LAN to Internet | Classroom PCs together |
🔹 Key Facts to Remember for CCNA
✅ Router works at OSI Layer 3.
✅ Uses IP addresses for decisions.
✅ Has a routing table.
✅ Can do static routing or dynamic routing.
✅ Provides inter-VLAN routing, NAT, ACLs, and WAN connections.
🔹 Do different VLANs/Subnets need a router?
- Devices in the same VLAN (same subnet) can talk directly through a switch.
- Devices in different VLANs (different subnets) cannot talk directly. They need help from a Layer 3 device.
🔹 How can different VLANs communicate?
You have two options:
- Router (traditional way – “Router on a Stick”)
- Each VLAN is connected to the router through a sub-interface.
- The router forwards traffic between VLANs.
- Good for small networks.
- Layer 3 Switch (modern way – Inter-VLAN routing)
- A Layer 3 switch can perform routing as well as switching.
- You create SVIs (Switch Virtual Interfaces) for each VLAN.
- The switch itself routes between VLANs.
- Faster and more scalable than using an external router.
🔹 Key Point for Beginners
- Switch only (Layer 2) → VLANs are isolated.
- Router or Layer 3 Switch → VLANs can communicate.
✅ For CCNA exam:
- You must know both methods:
- Router on a Stick (traditional).
- Inter-VLAN routing on a Layer 3 switch.
@learntechfromzero Learn CCNA for free. Explanation of a router and its role and functionality #ccna #router #internet #informationtechnology #networking ♬ original sound – Learn Tech From Zero