CCNA 200-301 v1.1 (Full Course)
1.1.b Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
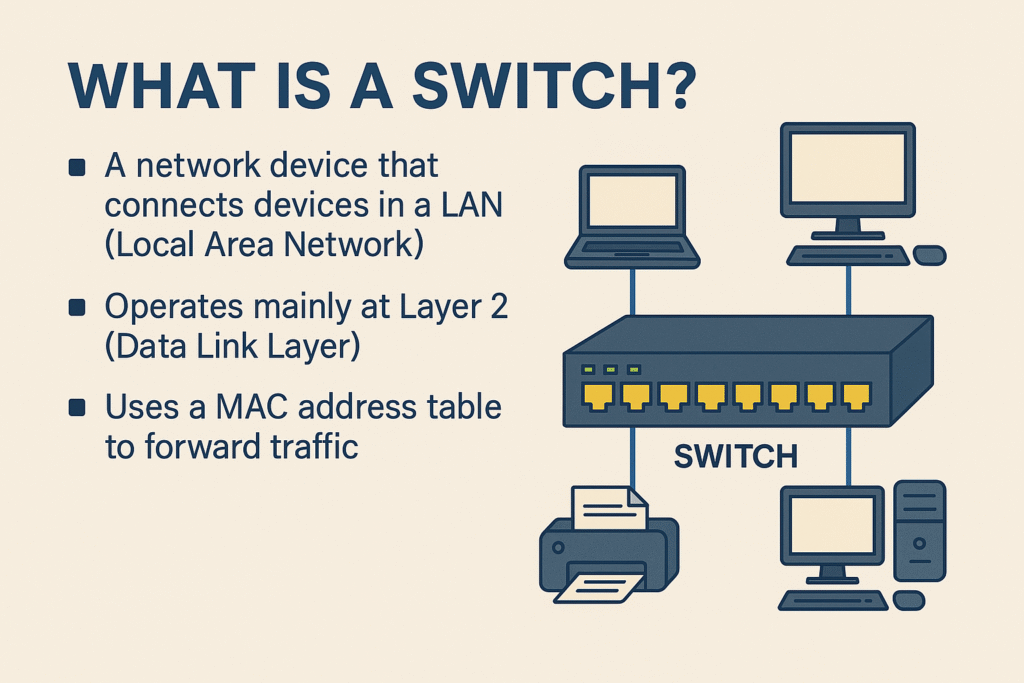
🔹 What is a Switch (basic recap)?
- A switch is a networking device that connects devices in a LAN.
- It works at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model (but some switches also work at Layer 3 (Network Layer)).
- Main job: Forward frames based on MAC addresses.
🔹 Layer 2 Switch
- Works at OSI Layer 2 (Data Link Layer).
- Makes decisions based on MAC addresses.
- Functions:
- Builds a MAC address table (switching table).
- Forwards frames within the same VLAN.
- Supports VLANs (but cannot route between them).
- Limitation:
- Cannot understand IP addresses.
- Cannot route between different subnets/VLANs.
- Example Use Case:
- Inside an office LAN where devices are on the same network.
👉 Think of it as a traffic controller for local devices.
🔹 Layer 3 Switch
- Works at both Layer 2 & Layer 3.
- Can perform all Layer 2 switch functions, plus routing (Layer 3) functions.
- Functions:
- Routes packets between different VLANs/subnets (Inter-VLAN routing).
- Uses IP routing protocols (like OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, static routes).
- Often faster than routers for internal LAN routing (since switching hardware is optimized).
- Limitation:
- Usually used inside LANs (not for WAN edge like routers).
👉 Think of it as a switch + router combined.
🔹 Key Differences (Layer 2 vs Layer 3 Switch)
| Feature | Layer 2 Switch | Layer 3 Switch |
|---|---|---|
| OSI Layer | Layer 2 (Data Link) | Layer 2 & 3 |
| Forwards using | MAC Address | MAC + IP Address |
| Inter-VLAN routing | ❌ Not possible | ✅ Possible |
| Routing protocols | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (OSPF, EIGRP, RIP, Static) |
| Typical Use | Basic LAN switching | Large LAN, VLAN-to-VLAN routing |
| Speed | High (hardware switching) | High (hardware + routing) |
🔹 Real Life Example
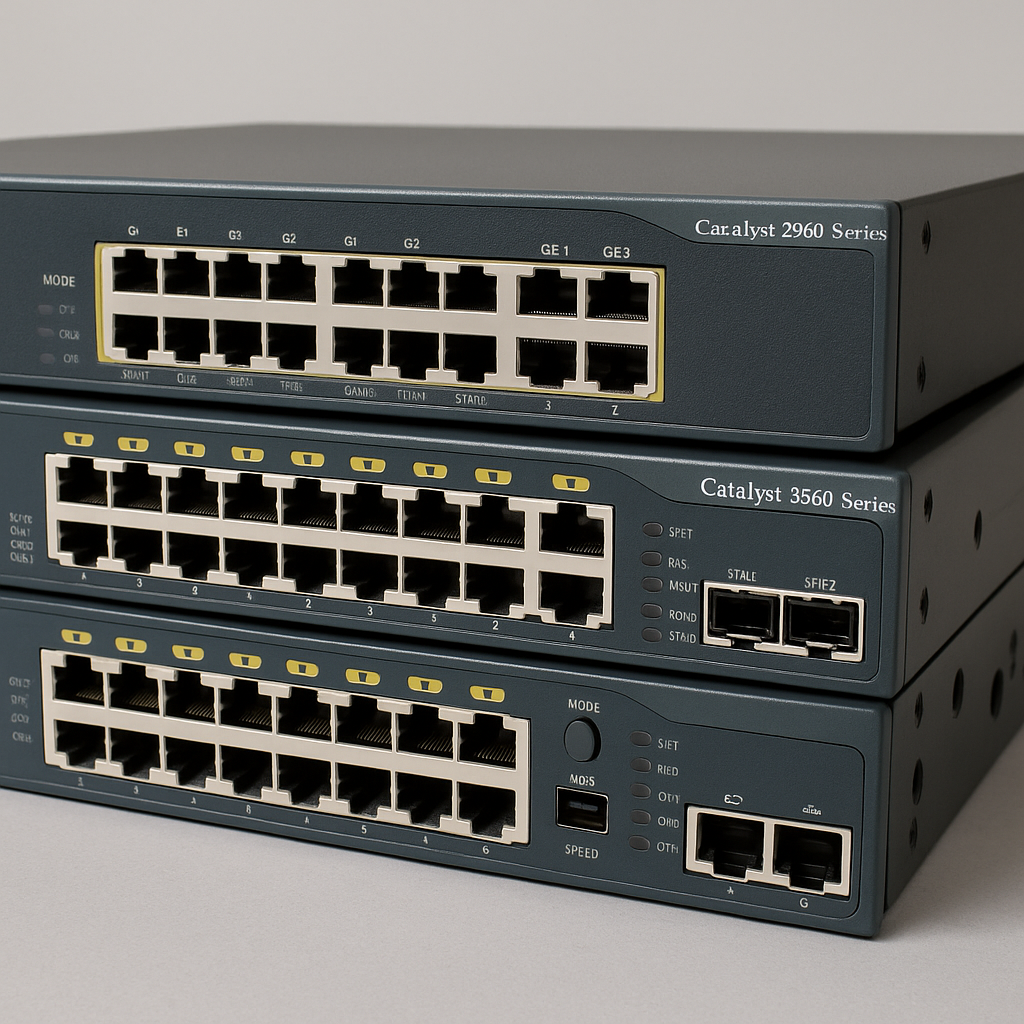
- Layer 2 Switch Example: Cisco Catalyst 2960 (only does switching).
- Layer 3 Switch Example: Cisco Catalyst 3560/3850 (does both switching and routing).
🔹 Exam Tips (CCNA)
✅ Remember: Layer 2 switch = MAC only, Layer 3 switch = MAC + IP.
✅ Routers vs Layer 3 switches: Both route between subnets, but routers are for WAN edge (internet, branch connections), while Layer 3 switches are for LAN inter-VLAN routing.
✅ Inter-VLAN routing can be done either:
- Using a router-on-a-stick (router + trunk link), OR
- Using a Layer 3 switch (SVIs = Switch Virtual Interfaces).
🔹 Unmanaged Switch
- Very basic switch.
- Just plug it in and it works.
- It only lets devices talk to each other on the same network.
- No settings, no VLANs, no security.
- Example: small cheap switch for home use.
👉 Think of it like a basic power strip: you just plug things in, no control.
🔹 Managed Switch
- A smart switch that you can configure.
- You can log in using CLI (commands), web page, or software.
- Supports:
- VLANs → separate groups of devices.
- Security → block or allow devices.
- Monitoring → check traffic, errors, logs.
- Quality of Service (QoS) → give priority to voice/video.
- Used in schools, companies, data centers.
👉 Think of it like a traffic light system: you control and manage the flow.
🔹 Quick Summary Table
| Type of Switch | Main Job | Can it do VLANs? | Can it route (connect VLANs)? | Who uses it? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unmanaged | Just connects devices | ❌ No | ❌ No | Home, small office |
| Managed (L2) | Smart switch using MAC | ✅ Yes | ❌ No | Schools, offices |
| Managed (L3) | Switch + Router | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes | Large LAN, enterprises |
@learntechfromzero CCNA full course. 1.1b Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching #switch #layer3switch #ccna #informationtechnology #computerscience ♬ original sound – Learn Tech From Zero